tests for lcl tear injury|why does my lcl hurt : manufacturer Most ligament injuries can be diagnosed with a thorough physical examination of the knee. Imaging Tests. Other tests that may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. Although they will not show any injury to your .
O artigo mergulhará nos detalhes sobre o grupo de crianças jogando futebol, a súbita aparição de um carro branco e o incidente assustador que deixou as crianças caídas. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBOctober's Very Own promo codes, coupons & deals, March 2024. Save BIG w/ (20) October's Very Own verified coupon codes & storewide coupon codes. Shoppers saved an average of $17.50 w/ October's Very Own discount codes, 25% off vouchers, free shipping deals. October's Very Own military & senior discounts, student discounts, reseller codes .
While most LCL tears can be diagnosed without medical imaging, a doctor may order an x-ray or MRI to rule out other possible injuries and to determine the severity of an LCL tear. X-ray. An x-ray shows bones and can help determine if there is a fracture.
Immediately following the injury, the RICE method is recommended: Rest. . Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) injuries of the knee typically occur due to a sudden varus force to the knee and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (ie. PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can . ACL and PCL tears are often confused with LCL injury due to shared nonspecific features like swelling, acute-onset pain, and knee instability. The anterior or posterior .Varus Stress Test- The most useful special test when assessing a LCL injury. With the femur stabilized, a varus force is applied with special attention to the lateral joint line. The test is first performed in 30 degrees flexion. Increased .
Most ligament injuries can be diagnosed with a thorough physical examination of the knee. Imaging Tests. Other tests that may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. Although they will not show any injury to your .Diagnosis of an LCL Injury. Your health care provider will first conduct a lateral collateral ligament test to reveal any looseness in the ligament. This test involves bending the knee to 25 degrees and placing pressure on the inside surface of .
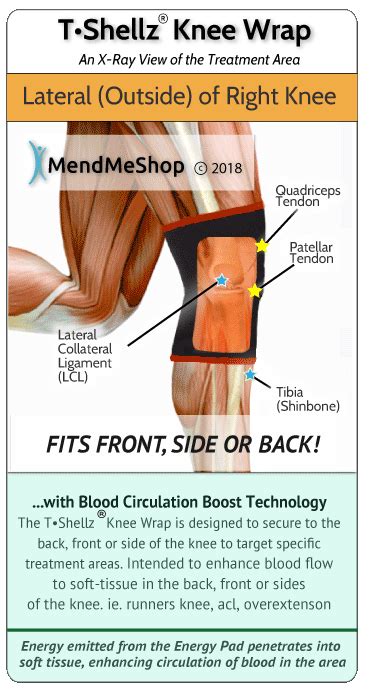
why does my lcl hurt
The incidence of LCL injuries are relatively low (6%) when compared to other knee injuries. It is commonly associated with other knee ligament injuries, thus LCL tear can be easily overlooked as a result of that. Mechanism of injury: . A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) tear is a knee injury that seldon happens in isolation. The force that causes it is usually so big that often something else also gets injured. This article explains how the LCL typically . Th LCL plays an important role in stabilizing the knee. Activities that put stress on this ligament, such as bending, twisting, or quickly changing direction, may lead to injuries of varying .
Isolated injuries of the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) are among the least common knee injuries but can occur when the joint is struck from the inside (varus stress). More commonly, and typically as the result of more significant trauma, the LCL is injured along with other structures, often including those of the posterolateral corner of .Medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprains are knee injuries. The MCL is the ligament located on the inside of your knee joint . It links your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) tear is a knee injury that seldom happens in isolation. The force that causes it is usually so big that something else al.A second test may be performed to examine the medial collateral ligament namely the Swain test. This test examines the chronic injury and rotatory instability of the knee. The test is performed by flexing the knee into 90 degrees and externally rotating the tibia. . (ACL) injuries, bone bruises, lateral collateral ligament injuries (LCL .
A strain or tear to the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is known as an LCL injury. The LCL is a band of tissue that runs along the outer side of your knee. It aids in keeping the bones together while you walk, ensuring that your knee joint remains stable. . The Knee Owner’s Manual provides a series of tests and clearly defined exercises .
Tears to the lateral collateral ligament most often occur from a direct blow to the inside of the knee. This can stretch the ligaments on the outside of the near too far and may cause them to tear. This type of injury occurs in sports. Lateral collateral ligament tears do not heal as well as medial collateral ligament tears do. Severe tears may require surgery.Varus Stress Test, tests for laxity of the Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL). Valgus Stress Test, tests for laxity of the Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL). Moving Valgus Stress Test, tests for chronic UCL sprain or tear from overuse (sensitivity: 100, specificity: 0.75). Modified Milking Maneuver, tests for UCL sprain or tear from overuse. The main cause of lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injuries is direct-force trauma to the inside of the knee. . What is a lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injury? . These tests will allow . A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprain occurs when there is a tear in the ligaments on the outside of the knee. Causes include sports injuries and accidents. Symptoms include pain, swelling .
PCL injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e PLC, ACL). Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with a traumatic knee effusion and increased laxity on a posterior drawer test but requires an MRI for confirmation. LCL Injury of the Knee . evaluate for meniscal or concomitant ligamentous injuries (McMurray, Dial test, varus/valgus stress) Neurovascular. evaluate peroneal function following high energy mechanisms and suspicion for multi-ligamentous injury pattern. Provocative tests. Lachman's test.
The lateral collateral ligament, or LCL, is one of the four major knee ligaments.The LCL connects the end of the thigh bone (the femur) to the top of the smaller shin bone (fibula), on the outside of the knee. The LCL helps to .An ACL tear is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in your knee. The recovery time is usually six to nine months after surgery. . Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). . You’ll probably need at least one of a few imaging tests, including: X-rays. A computed tomography (CT) scan. Tendon Conditions & Tears Distal Biceps Avulsion . Lateral Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury is a ligamentous elbow injury usually associated with a traumatic elbow dislocation, and characterized by posterolateral subluxation . In this video, we are demonstrating a Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injury Assessment, which looks for pain and injury to the outside knee. This test sho.
Varus stress test evaluates the lateral collateral ligament in the knee, assessing its stability and protection against outward forces. . These signs may suggest a tear or laxity in the LCL, indicating instability and likely an LCL injury. A negative test shows minimal lateral opening and a firm end feel, suggesting that the LCL is intact and .
Joint line tenderness: Joint line tenderness is a very non-specific test for a meniscus tear.The area of the meniscus is felt, and a positive test is considered when there is pain in this area. McMurray's test: This test is performed with the patient lying flat and the examiner bending the knee.A click can be felt over the meniscus tear as the knee is brought . See “ACL injury,” “PCL injury,” “MCL injury,” “LCL injury,” and “Meniscus injury” for subsequent management and details. Avoid knee immobilizers in isolated ligamentous injuries , as these can negatively affect treatment outcomes by decreasing quadriceps strength.
The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) is the primary varus stabilizer of the knee and isolated injuries are somewhat uncommon. . An increase in external rotation of more than 10 degrees with the knee flexed to 30 is indicative of a PLC injury. With the posterolateral drawer test, the examiner evaluates the PLC by applying a posteriorly .Most ligament injuries can be diagnosed with a thorough physical examination of the knee. Imaging Tests. Other tests which may help your doctor confirm your diagnosis include: X-rays. Although they will not show any injury to your anterior cruciate ligament, X-rays can show whether the injury is associated with a broken bone.
positive test is a subjective apprehension, instability, or pain at the MCL origin between 70 and 120 degrees . acceleration (70 degrees flexion), and location of late cocking (120 degrees flexion) 100% sensitive and 75% specific. LCL injuries. lateral pivot-shift test . patient lies supine with affected arm overhead; with shoulder fully .
PCL tear symptoms may include: Mild pain at the back of the knee that worsens when kneeling; Mild swelling; Pain in the front of the knee, particularly while running or slowing down; LCL Kneed Injury Symptoms. If you’ve injured your LCL, you’re most likely experiencing pain and swelling. Other common LCL tear symptoms include:
Symptoms vary depending on the grade of your LCL tear. Grade 1 tears come with minor pain and slight stiffness that will dissipate in about a week. . Your doctor will diagnose your injury by examining the area for swelling and by performing an LCL tear test. The test will consist of gently moving the knee in different directions to find the . Mid-substance tears can cause tenderness at the medial joint line, which can be confused with a medial meniscus injury. Distal MCL tears can cause tenderness at its attachment to the medial tibial condyle, which can be confused with pes anserine bursitis. Valgus stress testing is the best way to test the integrity of the MCL directly.

lcl tear test at home
Você pode assistir "Rambo - A Última Batalha" no Netflix, Globoplay, NOW, Netflix basic with Ads legalmente online, no Amazon Video alugar online .
tests for lcl tear injury|why does my lcl hurt